Jaký druh materiálu je EVA?
eva je kopolymer ethylene-vinyl acetátu materiál , je to nejtóxní, bezchutný, průhledný termoplast. Materiál eva má vynikající pružnost, flexibilitu, průhlednost, izolaci, odchylku při nízké teplotě, odolnost proti počasí, odolnost proti chemickému útoku, široce používán při výrobě materiálů pro dráty a kabely, plátna a další formované produkty a směsi, součásti automobilového průmyslu, lepidla, nátěry atd.

1. Složení a struktura materiálu eva
Kopoloemer: Ethylene znamená ethylen; Vinylacetate znamená vinyl acetát; Copolymer znamená kopoloemer; ethylene a vinyl acetát jsou dva monomery eva. Chemická strukturní formule eva je uvedena na následujícím obrázku:

Materiál eva je čtvrtou kategorií ethylenového kopoloemeru po vysokohustotním polyethylenu, nízkohustotním polyethylenu a nízkotlakém nízkohustotním polyethylenu. Ve srovnání s polyethylenem, kvůli přítomnosti polární funkční skupiny esterové vazby na boční řetězci materiálu eva, je krystalinita materiálu eva nižší a odolnost proti dopadům a počasí je výrazně zvýšena.
2. Způsob přípravy materiálu eva
V roce 1938 podala britská společnost ICI žádost o příslušný patent na eva kopolymér, a v roce 1960 byla začata hromadná výroba eva společností DuPont z USA. V současnosti existují čtyři metody výroby materiálů eva: vysokotlaké hromadné polymerizace, suspenzní polymerizace, emulzní polymerizace a polymerizace v roztoku.
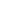
Mezi nimi je vysokotlaká hromadná polymerizace hlavní metodou pro výrobu materiálů EVA, přibližný proces je následující: v tlaku 1000 až 2000 standardních atmosférických tlaků a teplotě asi 100 ℃ se ethylenový plyn zavede do reaktoru s uvnitř obsaženou kapalnou vinylacetátovou součástí. Vinylacetát může sloužit jako reakční látko, ale také poskytuje řešivé prostředí pro reakci. Tento proces obvykle používá spojité tokové reakční zařízení, které umožňuje recyklovat vinylacetát, který nebyl zapojen do reakce, a pomocí této metody lze dosáhnout roční produkce více než 100 000 tun. Reakční zařízení pro materiál EVA je velmi podobné nízkohustotnímu polyetilenu (LDPE), jak je znázorněno na následujícím obrázku:
3. Klasifikace a aplikace materiálů EVA
Vlastnosti eva materiálů získaných různými polymerizačními metodami jsou docela odlišné a hlavní příčina spočívá v tom, že různé polymerizační metody ovlivňují obsah vinylacetátu v eva materiálech. Podle množství vinylacetátu se eva materiál dělí na eva rezinu, eva elastomer a eva emulzi.
Když je obsah vinylacetátu 5 % do 40 %, eva materiál vyrobený v této době se nazývá eva rezina, hlavně používaná jako folie na polní krytiny, pěnoviny a termofusibilní lepidlo. Běžné eva folie jsou následující:

Když je obsah vinylacetátu v eva materiálu 40 % do 70 %, tento eva materiál se nazývá eva guma a zvýšení obsahu esterových vazeb dává eva materiálu vysokou pružnost. V tomto okamžiku je eva materiál téměř nekristalický, teplota skla je velmi nízká a lze jej použít jako modifikátor PVC, jak je znázorněno na následujícím obrázku:

Pokud je použita eva materiál vyrobená emulzní polymerizací, může být obsah vinylacetátu až 70 % až 95 %, a eva materiál se v této době nazývá eva emulze. EVA emulze se převážně používá v oboru nátěrů, jako lepidlo a elektricky vodivá barva. Následující je typická eva emulze:

4. Vady a úprava eva materiálu
I když mají eva materiály mnoho vynikajících vlastností, eva je extrémně hořlavá a může produkovat jedovaté plyny. Abyste řešili problém hořlavosti eva materiálu a zajistili bezpečnost eva materiálu, nejúčinnější způsob je přidat k němu retardanty.
Dříve běžně používané brzdící látky byly halogenované brzdící látky. Mechanismus působení spočívá v tom, že když je brzdící látka ohřáta, rozkládá se na hydroxid halogenu a spotřebovává volná radikala vyprodukovaná při degradaci materiálu EVA, čímž přeruší řetězovou reakci materiálu EVA. Navíc je hydroxid halogenu těsný a hustý, což usnadňuje tvorbu "ochranné vrstvy" na povrchu materiálu EVA, snižuje plochu kontaktu mezi materiálem EVA a kyslíkem a má tak určitý účinek brzdícího působení.
Avšak hydroxid halogenu stále způsobuje sekundární znečištění a výzkumníci postupně začínají používat hydroxidy kovů, neorganické nanocástice a rozpínací brzdící látky jako materiály pro brzdící účinky na materiál EVA.